TL;DR
In this article, you will learn how to add a frontend to any LangGraph agent using the Agent User Interaction Protocol (AG-UI) developed by CopilotKit.
Before we jump in, here is what we will cover:
- Understanding AG-UI Protocol?
- Integrating LangGraph AI agents with AG-UI protocol
Lets dive in!
What is the AG-UI Protocol?
The Agent User Interaction Protocol (AG-UI), developed by CopilotKit, is an open-source, lightweight, event-based protocol that facilitates rich, real-time interactions between the frontend and AI agents.
The AG-UI protocol enables event-driven communication, state management, tool usage, and streaming AI agent responses.
To send information between the frontend and your AI agent, AG-UI uses events such as:
- Lifecycle events: These events mark the start or end of an agent’s work, like “The agent started processing your request” (
RUN_STARTED) or “The agent is done” (RUN_FINISHED). - Text message events: These events carry the actual conversation, like “The agent is starting a new message” (
TEXT_MESSAGE_START), “Here’s a piece of the response” (TEXT_MESSAGE_CONTENT), or “The message is complete” (TEXT_MESSAGE_END). - Tool call events: These events let the agent use tools, like “The agent wants to check the weather” (
TOOL_CALL_START) or “Here’s the weather data” (TOOL_CALL_END). - State management events: These events keep the frontend and the AI agent state in sync, like “Here’s the current state of the conversation” (
STATE_SNAPSHOT) or “Here’s a small update to the state” (STATE_DELTA).
You can learn more about the AG-UI protocol and its architecture here on AG-UI docs.
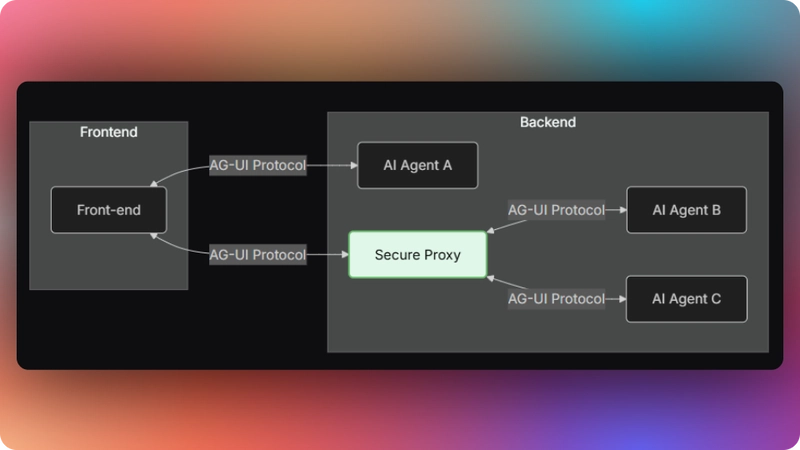
Now that we have learned what the AG-UI protocol is, let us see how to integrate it with different AI agent frameworks
Integrating LangGraph AI agents with AG-UI protocol
In this section, you will learn how to build a research assistant using the AG-UI protocol with LangGraph and CopilotKit's frontend framework. The system allows users to ask research questions and receive comprehensive reports based on web search results.
Here’s a preview of what we will be building:
Let’s jump in.
Building AG-UI LangGraph agent backend
To get started, make sure you have Python and Poetry installed on your machine. Then clone the AG-UI-LangGraph repository that consists of a Python-based backend (ag-ui-research-agent) and a Next.js/React frontend (ag-ui-research-frontend).
Next, navigate to the backend directory:
cd ag-ui-research-agentThen install the dependencies using Poetry:
poetry installAfter that, create a .env file with OpenAI and Serper API keys:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-key
SERPER_API_KEY=your-serper-keyThen run the agent using the command below:
poetry run uvicorn src.my_endpoint.main:appTo test the AG-UI LangGraph integration, run the curl command below on https://reqbin.com/curl.
curl -X POST [http://localhost:8000/langgraph-research](http://localhost:8000/langgraph-research) \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"thread_id": "test_thread_123",
"run_id": "test_run_456",
"messages": [
{
"id": "msg_1",
"role": "user",
"content": "Research lifespan of Penguins"
}
],
"tools": [],
"context": [],
"forwarded_props": {},
"state": {}
}'Let us now see how the AG-UI LangGraph integration works.
First, an endpoint with FastAPI that receives requests from the frontend using the RunAgentInput Pydantic model is created as shown in the src/my_endpoint/main.py file.
@app.post("/langgraph-research")
async def my_endpoint(input_data: RunAgentInput):
"""
Main AG-UI protocol endpoint for the research agent.
This endpoint:
1. Receives research queries from the frontend
2. Performs web searches using the Serper API
3. Processes and structures research results
4. Generates a comprehensive research report
5. Streams state updates and the final report back to the client
All communication follows the AG-UI protocol, using Server-Sent Events
for streaming responses with proper event encoding.
Args:
input_data (RunAgentInput): Contains conversation messages and run metadata
Returns:
StreamingResponse: Stream of AG-UI protocol events
"""Then an event encoder is created to properly format Server-Sent Events (SSE) according to the AG-UI protocol.
async def event_generator():
# Create an event encoder to properly format SSE events according to AG-UI spec
encoder = EventEncoder()After that, a run start event is sent using the RUN_STARTED lifecycle event.
# Step 1: Signal the start of the agent run
yield encoder.encode(
RunStartedEvent(
type=EventType.RUN_STARTED,
thread_id=input_data.thread_id,
run_id=input_data.run_id
)
)Then the state is initialized using the STATE_SNAPSHOT state management event.
yield encoder.encode(
StateSnapshotEvent(
message_id=message_id,
snapshot={
# Status section: Tracks the overall research process phase
"status": {
//...
},
# Research section: Information about the research process
"research": {
//...
},
# Processing section: Information about computational processing
"processing": {
//...
},
# UI section: Frontend display preferences
"ui": {
//... }
}
)
)Next, the agent state is updated using the STATE_DELTA state management event.
yield encoder.encode(
StateDeltaEvent(
message_id=message_id,
delta=[
{
//... },
# Update current research stage
{
//... },
# Indicate that processing is in progress
{
//...
},
# Set initial progress value
{
//... }
]
)
)After that, a research query is processed using a LangGraph research agent imported from the src/my_endpoint/langgraph_research_agent.py file.
# Build the research graph (LangGraph workflow)
graph = build_research_graph()
try:
print(f"[DEBUG] Executing LangGraph workflow")
# Execute the LangGraph workflow with the query
# Convert the AG-UI message to a LangChain message type
# Different LangGraph versions have different methods to run graphs
try:
# Try newer LangGraph API first
result = graph.invoke([HumanMessage(content=query)])
print(f"[DEBUG] LangGraph invoke API succeeded")
except AttributeError as e:
print(f"[DEBUG] LangGraph invoke API failed, trying older API: {str(e)}")
# Fall back to older LangGraph API
result = graph([HumanMessage(content=query)])
print(f"[DEBUG] LangGraph older API succeeded")
print(f"[DEBUG] LangGraph result type: {type(result)}, content: {str(result)[:100]}...")Then, text message events are sent to the frontend with the research report content.
# Send the text message with the report content
yield encoder.encode(
TextMessageStartEvent(
type=EventType.TEXT_MESSAGE_START,
message_id=message_id,
role="assistant"
)
)
yield encoder.encode(
TextMessageContentEvent(
type=EventType.TEXT_MESSAGE_CONTENT,
message_id=message_id,
delta=report_content
)
)
yield encoder.encode(
TextMessageEndEvent(
type=EventType.TEXT_MESSAGE_END,
message_id=message_id
)
)Next, a run-finished event is sent using the RUN_FINISHED lifecycle event.
# Complete the run
yield encoder.encode(
RunFinishedEvent(
type=EventType.RUN_FINISHED,
thread_id=input_data.thread_id,
run_id=input_data.run_id
)
)Finally, a streaming response containing SSE events from the event generator is returned.
# Return a streaming response containing SSE events from the generator
# The event_generator function yields events that are encoded according to the SSE protocol
# The media_type specifies that this is a stream of server-sent events
return StreamingResponse(
event_generator(),
media_type="text/event-stream"
)Building AG-UI LangGraph agent frontend using CopilotKit
In this section, you will learn how to create a connection between your AG-UI LangGraph backend and your app frontend using CopilotKit.
Let’s get started.
Step 1: Getting started
First, navigate to the frontend directory:
cd ag-ui-research-frontendThen install the dependencies:
cd ag-ui-research-frontendAfter that, start the development server:
npm run devNavigate to http://localhost:3000/copilotkit, and you should see the AG-UI LangGraph agent frontend up and running.
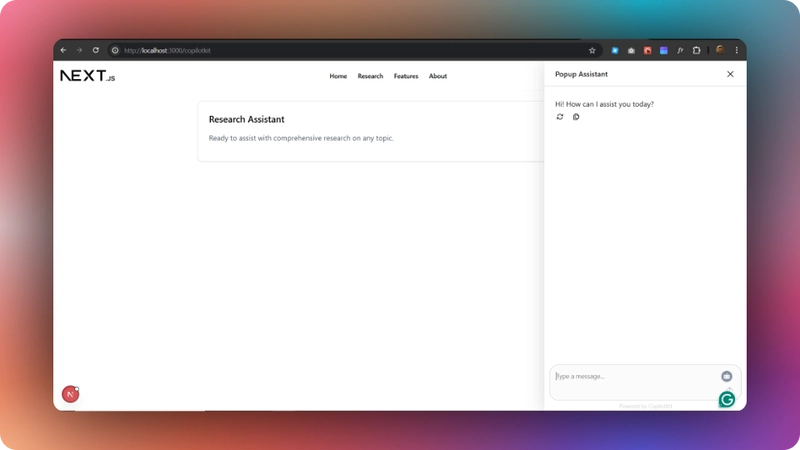
Let’s now see how to build the frontend UI for the AG-UI LangGraph agent using CopilotKit.
Step 2: Connecting frontend to AG-UI LangGraph backend
First, create a bridge that connects your frontend and the AG-UI LangGraph backend, as shown in the src/app/api/copilotkit/route.ts file.
// Import the HttpAgent for making HTTP requests to the backend
import { HttpAgent } from "@ag-ui/client";
// Import CopilotKit runtime components for setting up the API endpoint
import {{
CopilotRuntime,
ExperimentalEmptyAdapter,
copilotRuntimeNextJSAppRouterEndpoint,
}} from "@copilotkit/runtime";
// Import NextRequest type for handling Next.js API requests
import {{ NextRequest }} from "next/server";
// Create a new HttpAgent instance that connects to the LangGraph research backend running locally
const researchAgent = new HttpAgent({{
url: "http://127.0.0.1:8000/langgraph-research",
}});
// Initialize the CopilotKit runtime with our research agent
const runtime = new CopilotRuntime({{
agents: {{
researchAgent, // Register the research agent with the runtime
}},
}});
/**
* Define the POST handler for the API endpoint
* This function handles incoming POST requests to the /api/copilotkit endpoint
*/
export const POST = async (req: NextRequest) => {{
// Configure the CopilotKit endpoint for the Next.js app router
const {{ handleRequest }} = copilotRuntimeNextJSAppRouterEndpoint({{
runtime, // Use the runtime with our research agent
serviceAdapter: new ExperimentalEmptyAdapter(), // Use the experimental adapter
endpoint: "/api/copilotkit", // Define the API endpoint path
}});
// Process the incoming request with the CopilotKit handler
return handleRequest(req);
}};Step 3: Set up the CopilotKit Provider
To set up the CopilotKit Provider, the <CopilotKit> component must wrap the Copilot-aware parts of your application. For most use cases, it's appropriate to wrap the CopilotKit provider around the entire app, e.g., in your layout.tsx, as shown below in the src/app/copilotkit/layout.tsx file.
// Import the CSS styles for CopilotKit UI components
import "@copilotkit/react-ui/styles.css";
// Import React and ReactNode type for typing children prop
import React, { ReactNode } from "react";
// Import the CopilotKit provider component from the core package
import { CopilotKit } from "@copilotkit/react-core";
// Get the runtime URL from environment variables
// This URL points to the CopilotKit runtime API endpoint
const runtimeUrl = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_COPILOTKIT_RUNTIME_URL;
export default function Layout({ children }: {{ children: ReactNode }}) {{
return (
<CopilotKit
runtimeUrl={{runtimeUrl}} // URL for the CopilotKit runtime API
agent="researchAgent" // Specify which agent to use (matches the one defined in route.ts)
showDevConsole={false} // Hide the development console in production
>
{{children}}{" "}
{/* Render the child components inside the CopilotKit provider */}
</CopilotKit>
);
}}Step 4: Choose a Copilot UI
To set up your Copilot UI, first import the default styles in your root component (typically layout.tsx).
import "@copilotkit/react-ui/styles.css";Copilot UI ships with a number of built-in UI patterns; choose whichever one you like from CopilotPopup, CopilotSidebar, CopilotChat, or Headless UI.
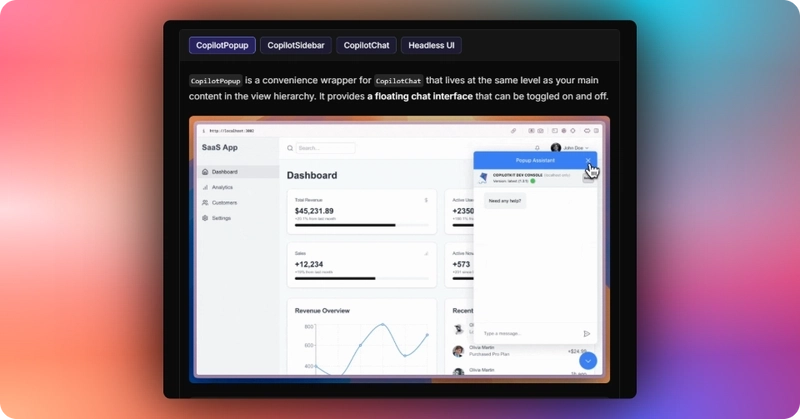
In this case, we will use CopilotChat defined in the src/app/copilotkit/page.tsxfile.
"use client";
import { CopilotSidebar } from "@copilotkit/react-ui";
import ResearchAssistant from "../components/Researcher";
import { Header } from "../components/Header";
export default function CopilotKitPage() {{
return (
<div className="flex flex-col min-h-screen">
<Header />
<main className="flex-1 container mx-auto px-4 py-6">
<ResearchAssistant />
<CopilotSidebar
clickOutsideToClose={true}
defaultOpen={false}
labels={{
title: "Popup Assistant",
initial: "Hi! How can I assist you today?",
}}
/>
</main>
</div>
);
}}Step 5: Creating a shared state between the frontend and AG-UI LangGraph backend
CoAgents maintain a shared state that seamlessly connects your UI with the agent's execution. This shared state system allows you to:
- Display the agent's current progress and intermediate results
- Update the agent's state through UI interactions
- React to state changes in real-time across your application
You can learn more about CoAgents’ shared state here on the CopilotKit docs.
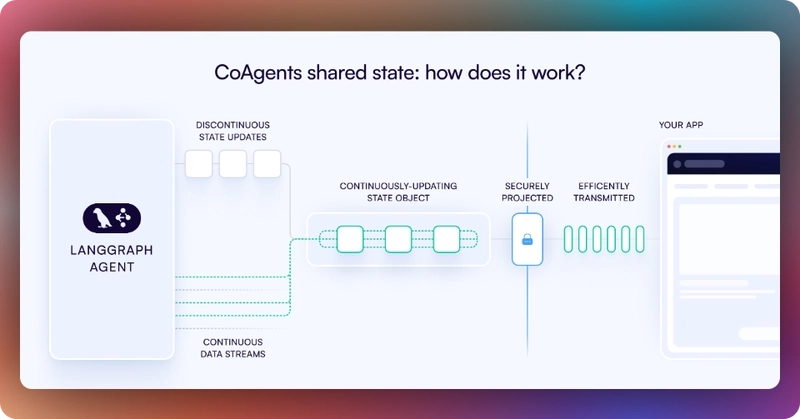
First, you need to define the agent state and emit it to the front end using the **STATE_SNAPSHOT** state management event to create a shared state between the frontend and AG-UI LangGraph agent backend.
yield encoder.encode(
StateSnapshotEvent(
message_id=message_id,
snapshot={{
"status": {{
"phase": "initialized", # Current phase of research process
"error": None, # Error tracking, null if no errors
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat() # When process started
}},
"research": {{
"query": query, # The user's original research question
"stage": "not_started", # Current research stage
"sources_found": 0, # Number of sources discovered
"sources": [], # List of research sources
"completed": False # Whether research is complete
}},
"processing": {{
"progress": 0, # Progress from 0.0 to 1.0
"report": None, # Final research report
"completed": False, # Whether processing is complete
"inProgress": False # Whether processing is ongoing
}},
"ui": {{
"showSources": False, # Whether to show sources panel
"showProgress": True, # Whether to show progress indicators
"activeTab": "chat" # Which UI tab is currently active
}}
}}
)
)Then use the CopilotKit useCoAgent hook to share the AG-UI LangGraph agent backend state with your frontend, as shown in the src/app/components/Researcher.tsx file.
import { useCoAgent} from "@copilotkit/react-core";
//...
function ResearchAssistant() {
// Connect to the agent's state using CopilotKit's useCoAgent hook
const { state, stop: stopResearchAgent } = useCoAgent<ResearchAgentState>({
name: "researchAgent",
initialState: {
status: { phase: "idle", error: null },
research: {
query: "",
stage: "not_started",
sources_found: 0,
sources: [],
completed: false,
},
processing: {
progress: 0,
report: null,
completed: false,
inProgress: false,
},
ui: { showSources: false, showProgress: false, activeTab: "chat" },
},
});
//...Next, render the AG-UI LangGraph agent's state in the chat UI. This is useful for informing the user about the agent's state in a more in-context way. To do this, you can use the useCoAgentStateRender hook.
import { useCoAgentStateRender } from "@copilotkit/react-core";
//...
function ResearchAssistant() {
// Implement useCoAgentStateRender hook
useCoAgentStateRender({
name: "researchAgent",
handler: ({ nodeName }) => {
// Stop the research agent when the "__end__" node is reached
if (nodeName === "__end__") {
setTimeout(() => {
isResearchInProgress.current = false; // Ensure flag is reset
stopResearchAgent();
}, 1000);
}
},
render: ({ status }) => {
if (status === "inProgress") {
isResearchInProgress.current = true;
return (
<div className="research-in-progress bg-white p-4 rounded-lg shadow-sm border border-gray-200">
<div className="flex items-center gap-2 mb-3">
<div className="animate-spin h-4 w-4 border-2 border-blue-500 rounded-full border-t-transparent"></div>
<p className="font-medium text-gray-800">
Research in progress...
</p>
</div>
<div className="status-container mb-3">
<div className="flex items-center justify-between mb-1.5">
<div className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-700">
{getStatusText()}
</div>
{state?.processing?.progress > 0 && (
<div className="text-xs font-medium text-blue-600">
{Math.round(state.processing.progress * 100)}%
</div>
)}
</div>
{state?.processing?.progress > 0 &&
state?.processing?.progress < 1 && (
<div className="h-1.5 w-full bg-gray-100 rounded-full overflow-hidden">
<div
className="h-full bg-blue-500 rounded-full transition-all duration-300"
style={{ width: `${state.processing.progress * 100}%` }}
/>
</div>
)}
</div>
{state?.research?.sources_found > 0 && (
<div className="text-xs text-gray-500 flex items-center gap-1.5">
<svg
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
width="12"
height="12"
viewBox="0 0 24 24"
fill="none"
stroke="currentColor"
strokeWidth="2"
strokeLinecap="round"
strokeLinejoin="round">
<path d="M15 3h4a2 2 0 0 1 2 2v14a2 2 0 0 1-2 2h-4M10 17l5-5-5-5M13 12H3"></path>
</svg>
Found {state.research.sources_found} source
{state.research.sources_found !== 1 ? "s" : ""}
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}
if (status === "complete") {
isResearchInProgress.current = false; // Ensure the flag is reset
// Don't return any UI here - let the main component handle showing the report
return null;
}
return null;
},
});Step 6: Streaming AG-UI LangGraph agent Response in the UI
To stream the research report content, use the ResearchReport component defined in the src/app/components/ResearchReport.tsx file in the src/app/components/Researcher.tsx file.
// When the research is complete and we have a report, show it
if (state?.status?.phase === "completed" && state?.processing?.report) {
return <ResearchReport state={state} />;
}Then navigate to http://localhost:3000/copilotkit, add “Research lifespan of penguins” to the chat, and press “Enter.” You should see the AG-UI LangGraph agent state rendered in the chat UI and the research report streamed in the UI, as shown below.
Conclusion
In this guide, we have walked through the steps of adding a frontend to any AI agents framework using AG-UI protocol and CopilotKit.
While we’ve explored a couple of features, we have barely scratched the surface of the countless use cases for CopilotKit, ranging from building interactive AI chatbots to building agentic solutions—in essence, CopilotKit lets you add a ton of useful AI capabilities to your products in minutes.
Hopefully, this guide makes it easier for you to integrate AI-powered Copilots into your existing application.
Follow CopilotKit on Twitter and say hi, and if you'd like to build something cool, join the Discord community.