The Agentic Application Stack Explained
The Agentic Application Stack Explained
Introduction
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence has ushered in a new era of applications that are not just smart but autonomous and interactive. Central to this evolution is the concept of agent-native applications—software designed around AI agents capable of understanding, learning, and acting autonomously to assist users in complex tasks. Examples like Replit’s Ghostwriter, OpenAI’s Canvas, and GitHub’s Copilot illustrate this paradigm shift towards agentic copilots that enhance productivity and user experience.
In this article, we’ll explore the Agentic Application Stack, the foundational architecture enabling these intelligent agents. We’ll delve into each layer of the stack, illustrating how they work together to create powerful, interactive applications. To make these concepts tangible, we’ll use a travel planning app as a running example, demonstrating how an AI agent can transform the user experience by automating itinerary creation, booking processes, and real-time adjustments.
Understanding Agent-Native Applications and Agentic Copilots
Before diving into the stack, it’s essential to grasp the broader design pattern of agent-native applications. These are applications where AI agents are not an add-on but a core component of the application’s functionality and user experience. Agentic copilots refer to AI agents that work alongside users, assisting them in tasks much like a human assistant would.
Applications like Replit’s Ghostwriter act as an intelligent coding assistant, OpenAI’s Canvas provides an interactive space where agents help organize thoughts and plans, and GitHub’s Copilot offers code suggestions in real-time. These tools exemplify how integrating AI agents at the core of application design can revolutionize user interaction and efficiency.
In our travel planning app example, an agentic copilot assists the user in planning their trip by understanding preferences, suggesting destinations, booking flights and accommodations, and even making adjustments based on real-time factors like weather or flight delays.
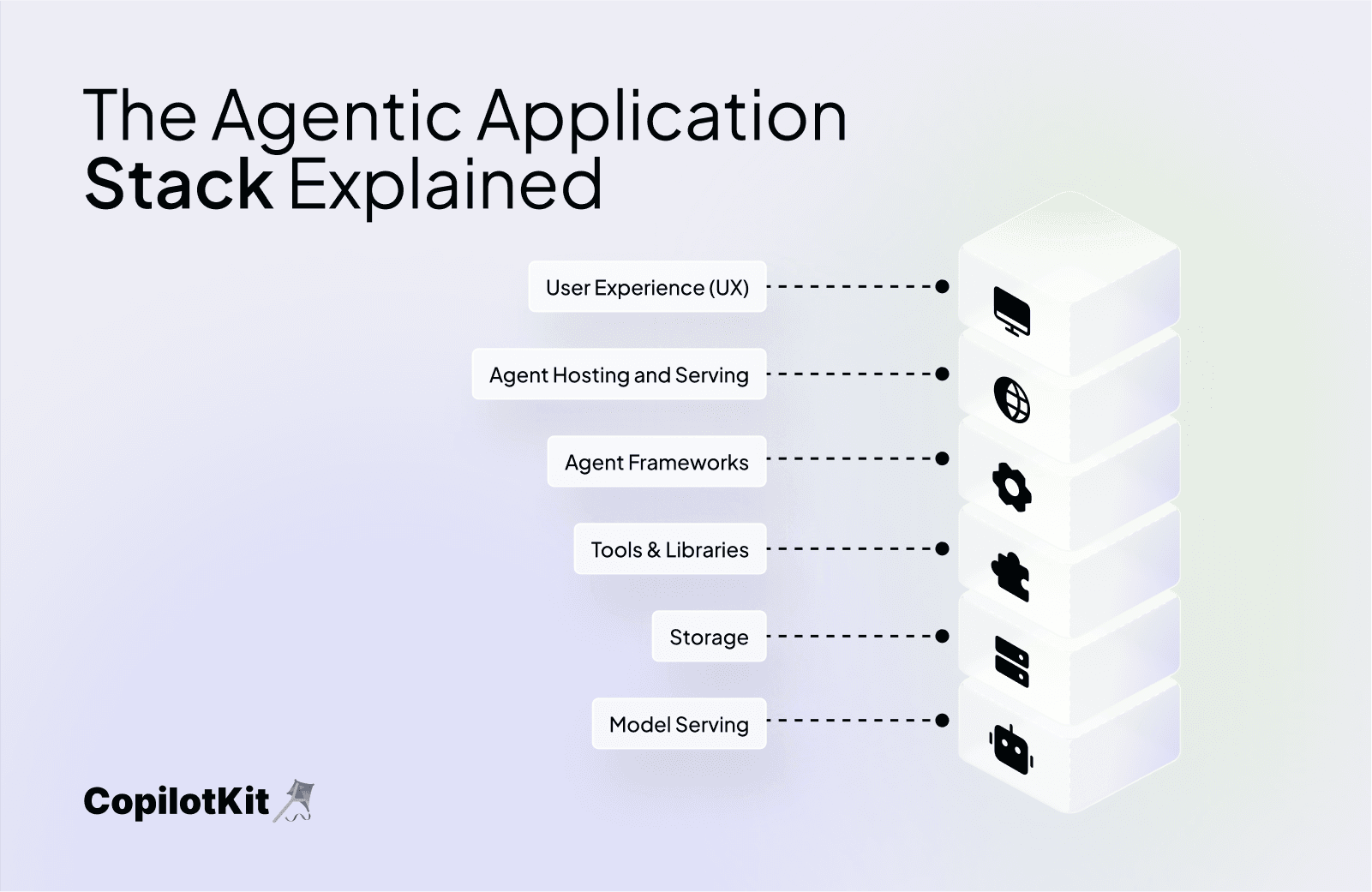
The Agentic Application Stack Overview
The Agentic Application Stack comprises several interconnected layers:
- Model Serving
- Storage
- Tools & Libraries
- Agent Frameworks
- Agent Hosting and Serving
- User Experience (UX)
Each layer plays a critical role in enabling the AI agent’s capabilities within an application. Let’s explore each layer in detail, integrating our travel planning app as an illustrative example.

1. Model Serving
a. Large Language Models (LLMs)
At the core of any AI agent is the Large Language Model (LLM). LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT-4, Anthropic’s Claude, or open-source models like Meta’s LLaMA provide the natural language understanding and generation capabilities that allow agents to interpret user inputs and generate appropriate responses.
In our travel app, the LLM enables the agent to understand user queries like “Plan a 7-day trip to Italy with a focus on historical sites” and generate detailed itineraries.
b. Model Providers and Inference Engines
- Closed API Providers: Services like OpenAI and Anthropic offer powerful models accessible via APIs. They handle the heavy lifting of hosting and maintaining the models, allowing developers to focus on application logic.
- Open-Source Models and Providers: Platforms like Hugging Face provide access to a variety of open-source models. Developers can fine-tune these models to better suit their application’s needs.
- Local Inference Engines: Tools like vLLM or Ollama allow developers to run models locally, which can be crucial for applications requiring data privacy or operating in environments with limited internet connectivity.
In the travel app, choosing between a cloud-based model or a local inference engine depends on factors like user privacy (handling personal travel preferences and payment information) and performance requirements.
2. Storage
a. State Management and Memory
Agents need to maintain context over interactions, which involves storing conversation history, user preferences, and other relevant data.
- Short-Term Memory: Handling immediate context, such as the current conversation thread.
- Long-Term Memory: Storing past interactions, preferences, and learned information for future reference.
In our travel app, the agent remembers the user’s past trips, preferred airlines, hotel chains, and dietary restrictions, enhancing personalization.
b. Databases
- Vector Databases: Tools like Pinecone, Weaviate, or Chroma store embeddings generated by LLMs, allowing efficient similarity search and retrieval. This is essential for agents to recall relevant information quickly.
- Relational Databases: Traditional databases like PostgreSQL (with extensions like pgvector) store structured data, such as user profiles, booking information, and transaction records.
- Hybrid Approaches: Combining both types of databases enables agents to handle unstructured data (like user queries) and structured data (like flight schedules) effectively.
In the travel app, when a user asks for hotel recommendations, the agent uses vector databases to match preferences with available options and relational databases to retrieve booking details.
3. Tools & Libraries
a. Tool Execution and Integration
Agents often need to perform actions that go beyond conversation, such as booking flights, checking weather forecasts, or accessing calendars.
- API Integrations: Agents interact with external services through APIs. For the travel app, this includes airlines, hotel booking platforms, and car rental services.
- Function Calling Mechanisms: Recent advancements allow LLMs to output structured data (like JSON) to call specific functions within the application. OpenAI’s function calling feature is an example, enabling agents to invoke application-specific logic.
b. Tool Libraries and SDKs
- LangChain: A popular framework that simplifies building applications with LLMs by providing tools for managing prompts, memory, and integrations.
- CopilotKit: Offers UI components that help developers create intuitive interfaces for agent interactions, ensuring users understand and can effectively guide the agent.
- OpenAI Plugins: Extend agent capabilities by allowing them to interact with third-party services securely.
In our travel app, the agent uses APIs to check flight availability, book hotels, or retrieve local attraction information. It might use a weather API to adjust plans if inclement weather is forecasted.
4. Agent Frameworks
a. Orchestration and Control Flow
Agent frameworks manage the flow of information between the user, the agent, and external services.
- Stateful Interaction Management: Frameworks like LangChain or Haystack help maintain conversation context and manage complex dialogues.
- Decision Making and Planning: Agents need to decide the sequence of actions to achieve user goals. This involves planning capabilities, which are crucial in multi-step tasks like travel planning.
b. Memory Management
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Combines LLMs with external knowledge bases to provide up-to-date and contextually relevant responses.
- Recursive Summarization: Summarizes long conversation histories to stay within LLM context window limits.
In the travel app, the agent uses these frameworks to handle conversations that span multiple sessions, ensuring it remembers past discussions about destinations or budget constraints.
5. Agent Hosting and Serving
a. Deployment Considerations
- Scalability: Hosting agents that can handle many users simultaneously requires scalable infrastructure. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud offer services to support this.
- Latency: For a smooth user experience, especially in interactive applications like our travel app, low-latency responses are crucial.
b. Secure Execution
- Data Privacy: Handling personal data requires compliance with regulations like GDPR. Secure hosting environments and data encryption are essential.
- Tool Execution Security: Agents executing actions (like booking a flight) must do so securely, ensuring transactions are safe and authorized.
c. API Access and Integration
- RESTful APIs: Exposing agent functionalities via APIs allows integration with other applications or services.
- WebSockets and Streaming: For real-time updates (e.g., flight price changes), streaming capabilities provide immediate feedback to the user.
In our travel app, agent hosting ensures that the agent can handle peak usage times (like holiday seasons) without degradation in performance and that all transactions are secure.
6. User Experience (UX)
a. Importance of UX in Agentic Applications
The UX layer is where the user interacts directly with the agent. A well-designed UX is critical for:
- Transparency: Users should understand what the agent is doing and why.
- Control: Users need to guide the agent, correct it, or provide additional information.
- Trust: A clear and intuitive interface builds trust in the agent’s capabilities.
b. Designing for Agentic UX
- Conversational Interfaces: Utilizing chat-based UIs where users communicate with the agent naturally.
- Visualizations: Showing the agent’s reasoning paths, suggested itineraries, or decision-making processes helps users follow along.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Allowing users to provide feedback or rate suggestions improves the agent’s future interactions.
c. Challenges and Solutions
- Complexity Management: Agents handle complex tasks; simplifying this for users is key.
- Dynamic Content: The interface must adapt to changing information, like flight availability.
- Accessibility: Ensuring the app is usable by people with varying abilities and preferences.
In the travel app, UX components might include an interactive map showing suggested routes, a calendar view of the itinerary, or notifications about changes (e.g., flight delays).
d. Tools for Enhancing UX
- CopilotKit: Provides pre-built UI components tailored for agent interactions, reducing development time and ensuring best practices.
- Microsoft’s Bot Framework Composer: Offers tools for designing conversational experiences.
- Flutter and React Native: Enable cross-platform app development, ensuring a consistent UX on mobile and web.
Integrating the Layers: The Travel Planning App in Action
Bringing all layers together, here’s how our travel planning app leverages the Agentic Application Stack:
- Model Serving: The LLM interprets user requests like “Plan a romantic getaway to Paris next month” and generates appropriate responses.
- Storage: The agent accesses stored preferences, knows the user’s budget, and remembers past trips to avoid repetition.
- Tools & Libraries: It uses APIs to check flight schedules, hotel availability, and local events, integrating suggestions into the conversation.
- Agent Frameworks: Manages the dialogue flow, ensuring the agent asks clarifying questions if needed (e.g., “Do you prefer a hotel or an Airbnb?”).
- Agent Hosting and Serving: The application scales to handle many users, maintains secure transactions, and provides real-time updates.
- User Experience: The user interacts with the agent via a chat interface, views suggested itineraries on a map, and can approve or modify plans easily.
The Broader Impact of Agentic Copilots
The travel planning app is just one example of how agentic copilots can transform user experiences across industries:
- Coding Assistants: Replit’s Ghostwriter helps developers by suggesting code snippets and debugging.
- Design Tools: OpenAI’s Canvas allows users to organize ideas spatially with AI assistance.
- Software Development: GitHub’s Copilot accelerates coding by providing real-time code suggestions within the IDE.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of the Agentic Application Stack and its potential to revolutionize how we interact with technology.
Conclusion
The Agentic Application Stack represents a comprehensive framework for building intelligent, interactive applications centered around AI agents. By understanding each layer—from the foundational LLMs to the critical UX design—we can create applications that are not only powerful but also user-friendly and impactful.
Incorporating agent-native design patterns, as seen in leading-edge tools like Replit’s Ghostwriter and GitHub’s Copilot, highlights the shift towards more integrated and autonomous AI assistance in software.
For developers and businesses looking to harness the power of AI agents, focusing on the entire stack is essential. Tools like CopilotKit can aid in developing the UX layer, while frameworks like LangChain assist with agent orchestration.